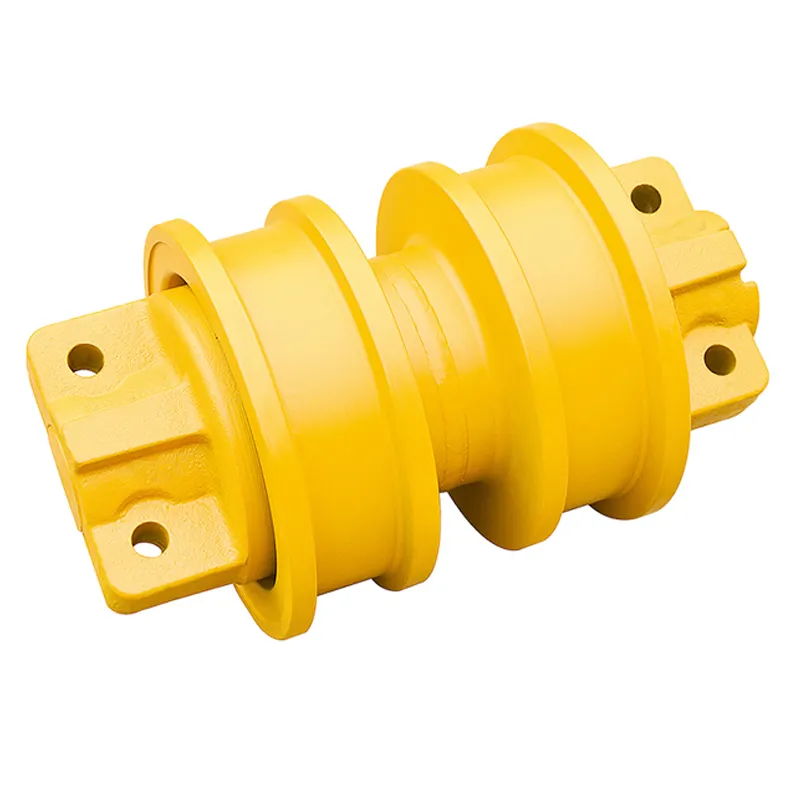
Understanding Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator Function and Common Failure Modes
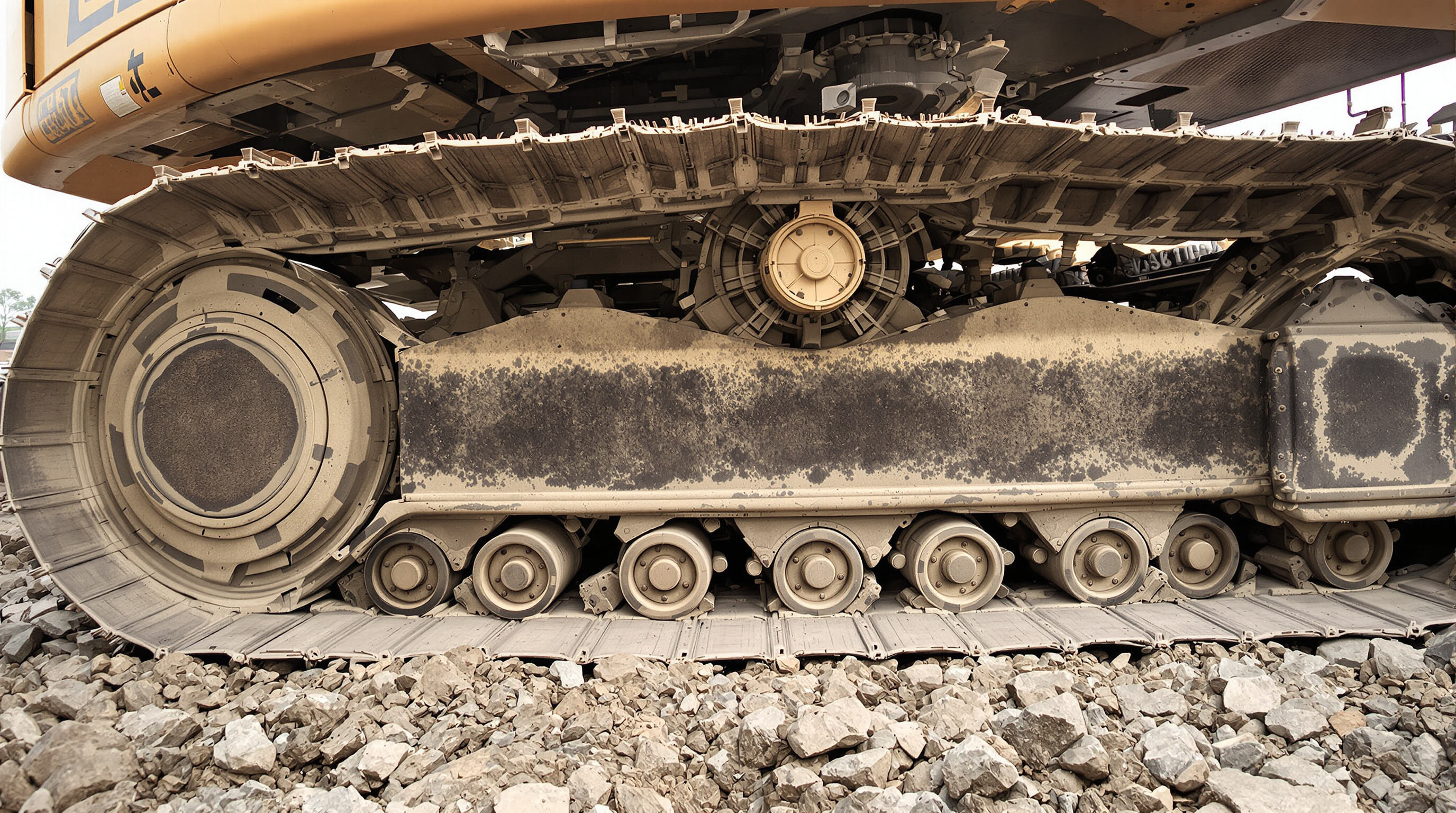

Anatomy and Function of a Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator Undercarriage Systems
Track rollers play a vital role as load bearing parts in all sorts of heavy equipment, taking on about three quarters of what an excavator weighs while keeping the track chain moving smoothly along the undercarriage. These components typically feature hardened steel rings on the outside, some sealed bearings inside, plus axle parts that let them spin with the track itself. The way they work helps spread out pressure from the ground more evenly across the machine. There are also internal channels for grease delivery, which cuts down on direct metal contact between parts. This reduces heat buildup from friction and slows down when things start wearing out too fast. According to industry reports from Ponemon back in 2023, proper maintenance of these systems makes a big difference in how long machines stay operational before needing repairs.
Differentiating Single and Double Flange Track Rollers for Bulldozer Excavator Applications
| Flange Type | Load Distribution | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Single Flange | Centralized force on flat terrain | Light-duty excavators |
| Double Flange | Lateral stability on slopes/uneven ground | Bulldozers and mining excavators |
| Double flange rollers extend service life by 20-30% in high-stress environments by preventing track derailment. Single-flange models offer a cost-effective solution for paved or predictable construction sites. |
How Track Rollers Differ From Carrier Rollers in Structure and Role
While both support the track chain, carrier rollers have a narrower profile and handle vertical loads only. Track rollers for bulldozer excavators feature wider bases and reinforced flanges to manage radial forces from machine weight, axial forces during slope operations, and shock loads from rough terrain.
Common Failure Modes and Mechanical Consequences of Worn Track Rollers
A 2024 industry study found that 68% of undercarriage failures originate from track roller issues, primarily due to:
- Bearing seizure: Causes erratic track movement and accelerates sprocket wear
- Flange erosion: Increases risk of track misalignment and derailment
- Axle deformation: Reduces load capacity by 40% and strains adjacent components
- Grease contamination: Water ingress increases friction by 300%, leading to rapid metal fatigue
Neglected roller wear can cut track chain life in half and raise fuel consumption by 18% due to increased drive motor load.
Identifying Failure Signs and Conducting Undercarriage Inspections
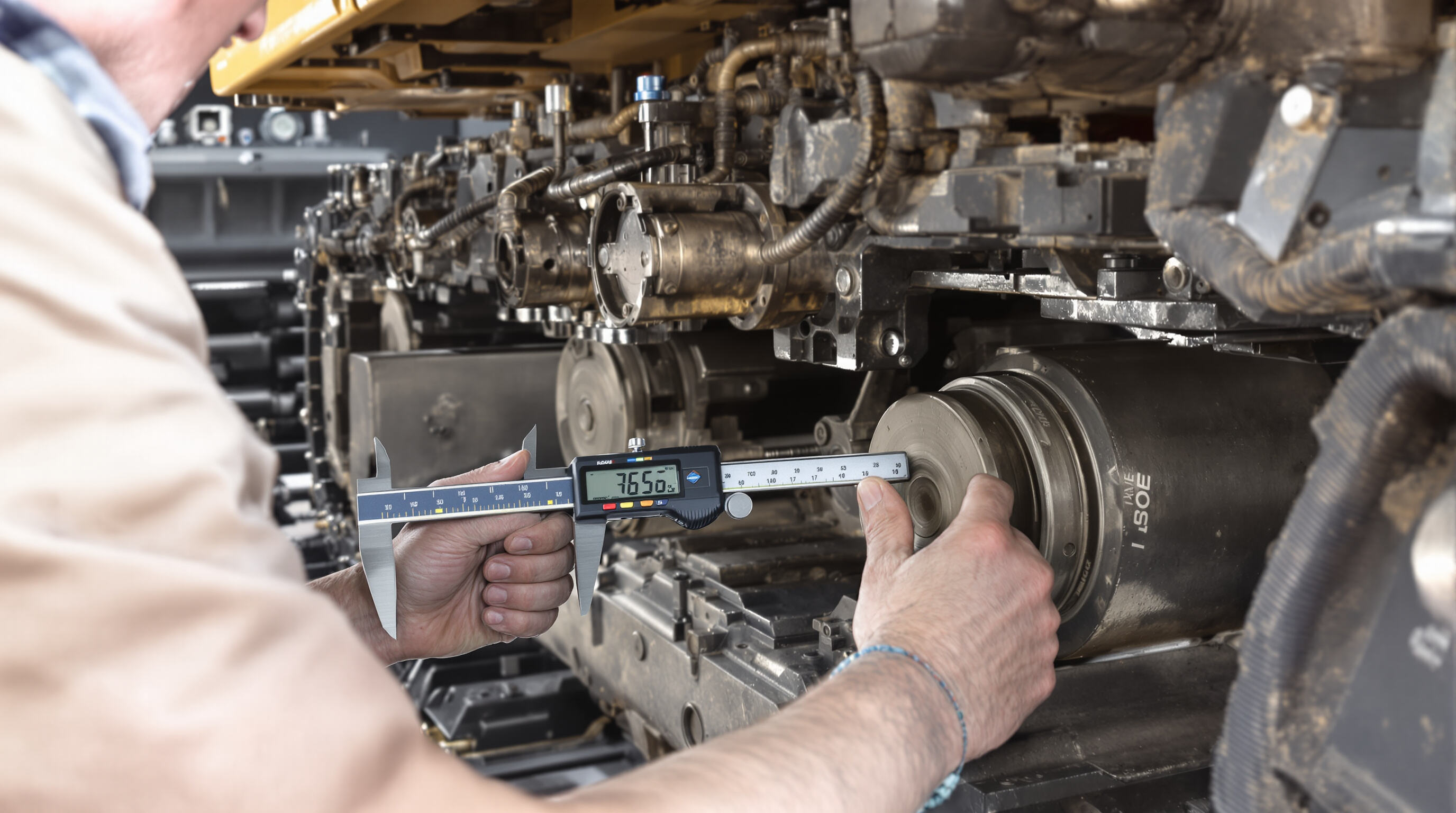
Key signs of track roller failure in bulldozer and excavator models
Operators should monitor for uneven track wear, abnormal vibrations, metallic grinding noises, and reduced maneuverability—especially during turns. Visible flange erosion exceeding 5-7mm height loss indicates advanced wear. Early detection is critical, as 68% of tracked equipment showed roller-related issues before full undercarriage breakdowns (2023 undercarriage analysis).
Inspection techniques and wear measurement standards for track rollers
Effective inspections combine three methods:
- Visual assessment: Look for cracks, pitting, or uneven contact patterns
- Dimensional verification: Measure flange thickness and roller diameter using calipers against OEM specs
- Functional testing: Manually rotate rollers to check for binding or resistance
Replace components when wear exceeds 10% of original dimensions. Always refer to manufacturer-specific wear charts for Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator models.
Checking axle and surrounding components for secondary damage
Use a bore gauge to inspect axle seats for scoring or ovalization—distortions as small as 0.5mm can accelerate new roller wear. Evaluate adjacent parts:
- Sprocket teeth for hooking (replace if wear ≥4mm)
- Idler wheels for rim deformation
- Track links for bushing wear exceeding 3mm
Document findings in a standardized format:
| Component | Allowable Wear | Measurement Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Roller Flange | ≤8mm | Digital Caliper |
| Axle Bore | ≤0.3mm | Bore Gauge |
| Track Link Pin | ≤2.5mm | Wear Gauge Set |
Clean roller cavities with solvent before reassembly and torque axle nuts to OEM specifications (±5% tolerance) using a calibrated torque wrench.
Preparing Tools, Materials, and Correct Replacement Components
Essential Tools and Materials for Track Roller Replacement
Successful replacement requires:
- Hydraulic jacks (10-30 ton capacity)
- Torque wrench (300-600 Nm range)
- Bearing press kit
- High-temperature grease (NLGI #2 or equivalent)
- ISO 898-1 Class 10.9 bolts
Safety gear—including steel-toe boots and hydraulic lockout devices—is essential. Inadequate tool preparation contributes to 34% of undercarriage-related injuries (2023 Equipment Maintenance Report).
Selecting the Correct Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator Compatibility
Choose replacements based on flange type (single/double) and axle diameter (±1 mm tolerance). For excavators under 20 tons, double-flange rollers provide 23% better lateral load distribution. Confirm compatibility using OEM diagrams for:
- Roller width (typically 150-250 mm for mid-sized units)
- Seal type (labyrinth vs. lip seals)
- Hardness rating (55-60 HRC for standard use)
Ensuring Part Compatibility With Trusted Suppliers
Source components meeting OEM specifications for metallurgy and dimensional accuracy. Reputable suppliers comply with ISO 286-2 tolerance standards, reducing premature wear by up to 40% in field tests. For critical applications, request certified material test reports (MTRs) confirming alloy composition (e.g., 42CrMo4/4140 steel).
Pro Tip: Maintain a "compatibility checklist" with equipment serial numbers, service history, and prior part batches.
Safety Protocols and Proper Excavator Lifting Procedures
Critical Safety Precautions During Undercarriage Maintenance
Before starting any work, it's essential to put lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures into place so equipment doesn't accidentally start running while someone is working on it. Safety gear matters too. Workers should definitely have those ANSI approved items like steel toe boots, heavy duty gloves, and proper eye protection when operating near machinery. When setting up an excavator, make sure it sits firmly on flat ground. Use outriggers if available or good quality timber blocks underneath. According to a study published in the Occupational Safety Journal back in 2022, nearly one quarter of all undercarriage injuries happen because machines weren't properly stabilized. Don't forget to check hydraulic systems regularly for any signs of leakage as well. Even small drips can lead to major problems during lifting operations, which nobody wants to deal with mid-job.
Safe Excavator Lifting and Support Techniques to Prevent Accidents
Always check the equipment's load chart first and make sure to lift at those manufacturer approved jacking points. We've seen too many problems where hydraulic cylinders failed, actually causing 17% of all excavator collapses last year because weight wasn't properly distributed across the machine. When supporting the equipment, go with at least 20-ton jack stands paired with solid 4 inch steel cribbing blocks for extra stability. Safety first folks! Keep everyone outside a 15 foot radius while doing any lifting work and don't forget about following those OSHA guidelines for heavy equipment maintenance including proper load testing procedures and making certain operators are certified. Before getting that brand new Track Roller for the Bulldozer Excavator up and running, double check everything is stable on either compacted gravel or solid concrete surfaces to avoid any unexpected issues down the road.
Executing the Track Roller Replacement and Post-Installation Checks
Step-by-Step Removal of the Damaged Track Roller
Start by loosening up that track tensioner so there's enough room to work. Next, get the undercarriage lifted off the ground with a good quality hydraulic jack and then prop it securely on those heavy duty stands everyone recommends for this job. When taking out those mounting bolts, grab an impact wrench and pay attention to how they're positioned and in what order they came out. Some bolts can be real trouble if they've been stuck for ages. Give them a good shot of penetrating oil first and let it sit for around ten to fifteen minutes before trying again. Don't forget to check the axle shaft for any signs of scoring or galling either. Believe it or not, a lot of early roller failures happen because people miss these issues on the axle. Industry folks say about 32 percent of all premature failures come down to overlooked axle damage according to their latest survey findings last year.
Installing the New Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator and Securing Hardware
Align the replacement roller with the axle, ensuring correct flange orientation. Hand-tighten bolts in a star pattern, then torque to 450-500 Nm using a calibrated wrench—exceeding this range increases bearing stress by 18% (Journal of Construction Machinery, 2022). Verify free rotation by manually spinning the roller before lowering the machine.
Following Manufacturer Guidelines for Proper Replacement Procedures
Adhere to the OEM’s break-in protocol, typically involving 30 minutes of low-speed, no-load operation to allow proper bearing seating. Modern service manuals recommend laser alignment checks during installation, a practice adopted by 67% of tracked equipment shops to extend component lifespan.
Lubrication, Cleaning, and Final Inspection After Replacement
Lubricate all zerk fittings with high-temperature lithium-complex grease until fresh grease purges from seals. Wipe away excess to prevent dirt accumulation—contamination causes 41% of lubrication-related failures. Inspect adjacent carrier rollers and idlers, replacing any with over 3mm flange wear.
Test Operation and Verification of Undercarriage Performance
Operate the excavator over mixed terrain for 15-20 minutes, monitoring for irregular track slap or lateral drift. Measure track tension in cold and hot conditions, adjusting to maintain a 25-30 mm sag difference per manufacturer guidelines. Record all data to establish a baseline for future inspections.
FAQs
What is the main function of a track roller in an excavator?
Track rollers support the load and ensure smooth movement of the track chain along the undercarriage, distributing pressure across the machine's structure.
What is the difference between single and double flange track rollers?
Single flange rollers are suited for flat terrains, whereas double flange rollers offer better lateral stability for slopes and uneven grounds, making them ideal for bulldozers and mining applications.
How can you identify signs of track roller failure?
Signs include uneven track wear, abnormal vibrations, metallic noises, and reduced maneuverability, particularly during turns.
Why is it important to follow manufacturer guidelines during track roller replacement?
Adhering to guidelines ensures proper installation, extends component lifespan, and prevents premature failures.
Table of Contents
-
Understanding Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator Function and Common Failure Modes
- Anatomy and Function of a Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator Undercarriage Systems
- Differentiating Single and Double Flange Track Rollers for Bulldozer Excavator Applications
- How Track Rollers Differ From Carrier Rollers in Structure and Role
- Common Failure Modes and Mechanical Consequences of Worn Track Rollers
- Identifying Failure Signs and Conducting Undercarriage Inspections
- Preparing Tools, Materials, and Correct Replacement Components
- Safety Protocols and Proper Excavator Lifting Procedures
-
Executing the Track Roller Replacement and Post-Installation Checks
- Step-by-Step Removal of the Damaged Track Roller
- Installing the New Track Roller for Bulldozer Excavator and Securing Hardware
- Following Manufacturer Guidelines for Proper Replacement Procedures
- Lubrication, Cleaning, and Final Inspection After Replacement
- Test Operation and Verification of Undercarriage Performance
- FAQs