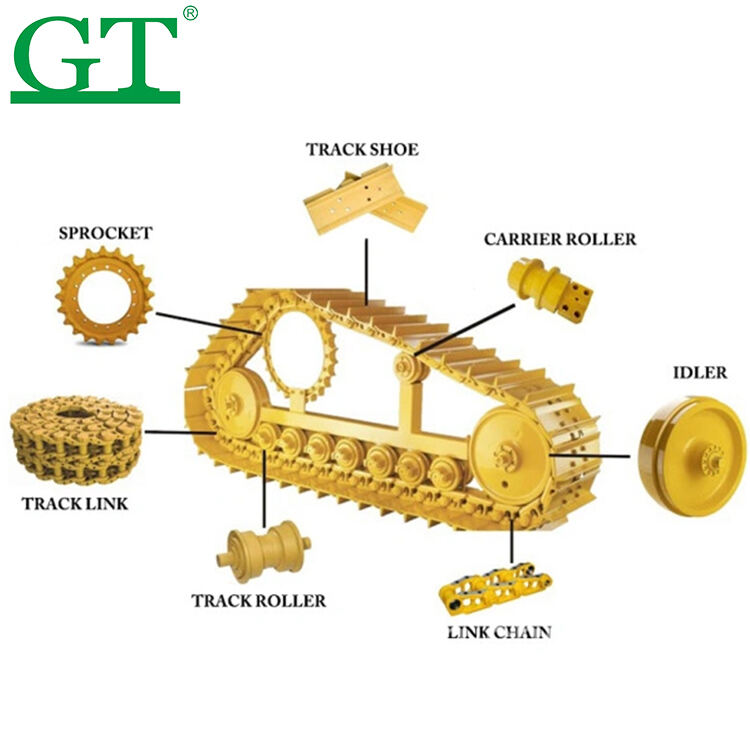
Early detection of track chain wear prevents catastrophic undercarriage failures. Focus on these three critical indicators:
- Elongation exceeding operational limits
- Deterioration of load-bearing components (link plates, bushings)
- Irregular tension loss patterns
Chains operating beyond wear specifications reduce machine lifespan by 40% and increase annual maintenance costs by $18k per machine (Construction Tech Journal, 2023). Proactive monitoring prevents secondary damage to sprockets, rollers, and idlers.
Elongation Measurement Thresholds
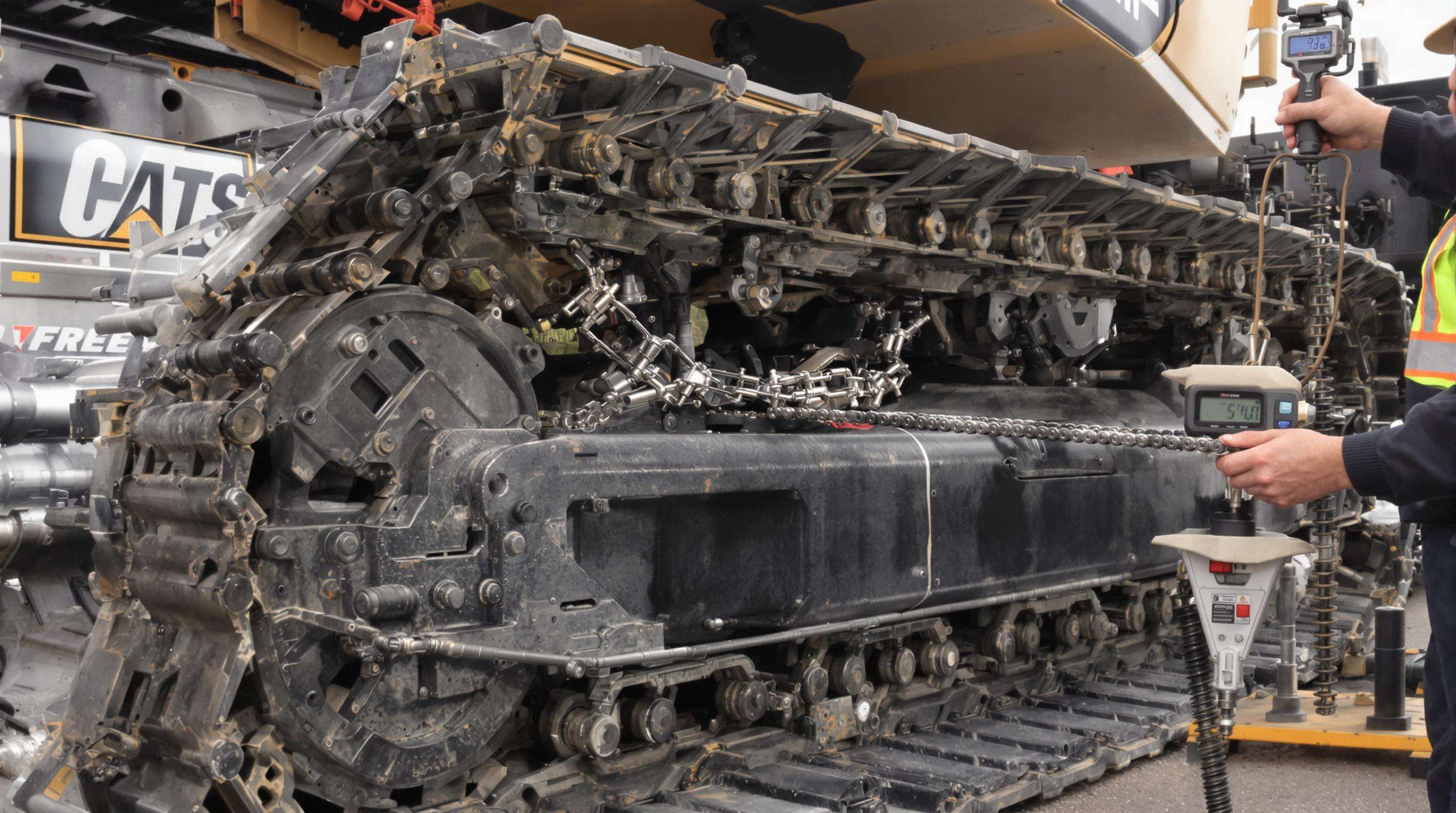

Chain elongation—stretch between pins and bushings—directly impacts sprocket engagement. Data from 20-ton excavator studies shows chains exceeding 3% elongation accelerate roller wear by 57%. Follow these operational thresholds:
| Machine Weight Class | Max Safe Elongation | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| <15 tons | ≤2.5% | Moderate wear |
| 15-30 tons | ≤3.0% | Critical inspection |
| 30+ tons | ≤3.5% | Immediate replacement |
Measure with calibrated tension gauges at three chain sections. Exceeding limits increases derailment risks by 70% even in visually intact chains.
Visual Inspection of Link Plates and Bushings
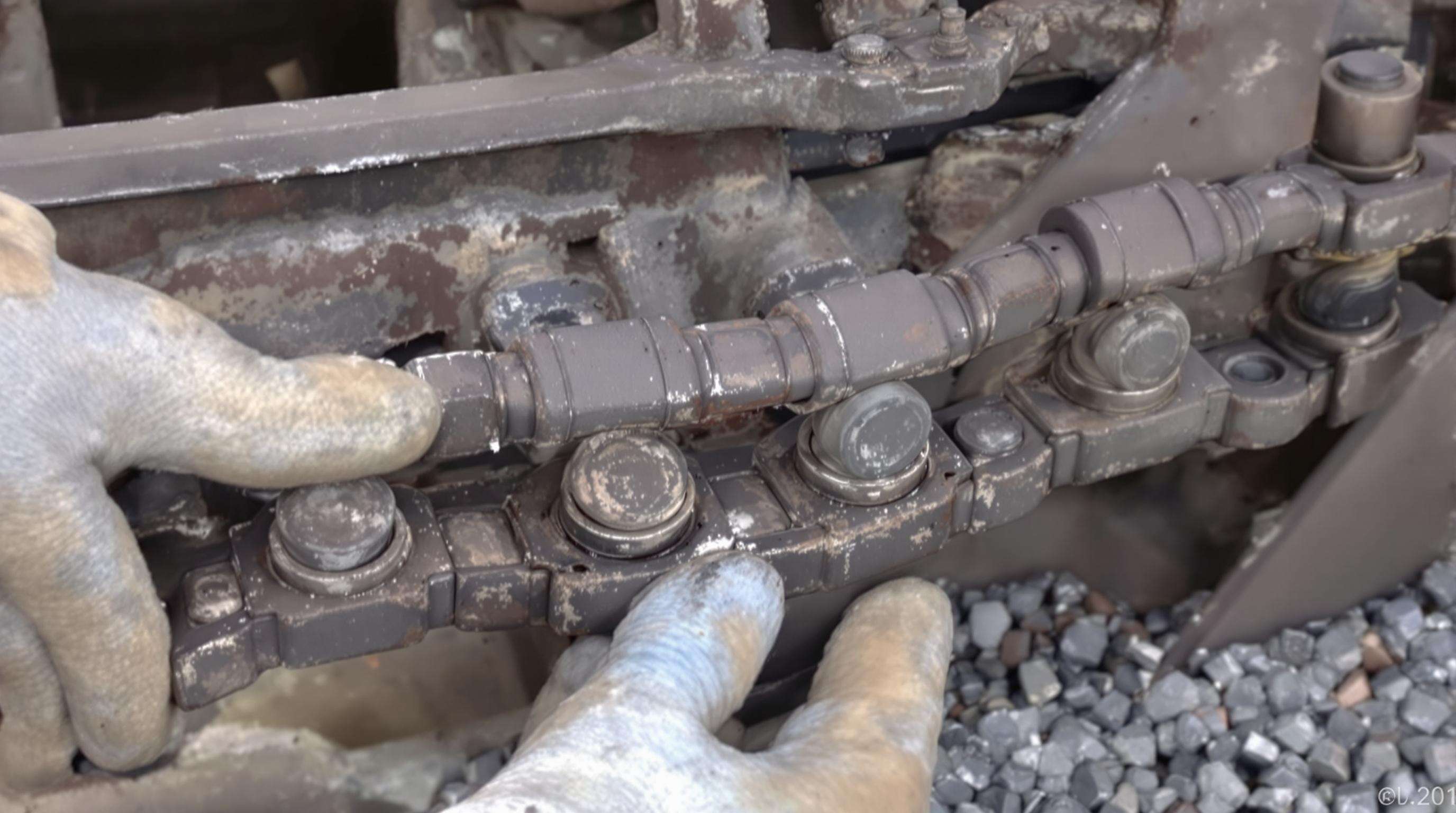

Monthly inspections should target:
- Link plates: Hairline fractures near pin holes and uneven guide lug wear
- Bushings: Flattening exceeding 25% of original height or discoloration
- Pin rotation: Grooves from fixed pins creating stress points
Exposed base metal requires immediate replacement—oxidized surfaces increase track slippage by 80%. Document findings with wear mapping.
Premature Track Tension Loss Patterns
Watch for:
- Re-tensioning needed every 50 hours (standard: 200 hours)
- Left/right tension imbalance >10%
- Seasonal fluctuations beyond manufacturer specs
These symptoms correlate with 15% fuel efficiency drops and traction loss during inclines.
DIN 22252-3 Standard for Sprocket Profile Checks
The DIN 22252-3 standard measures:
- Tooth curvature depth
- Pressure angle conformity
- Flank wear symmetry
Deviations beyond 3% tolerance indicate early "hook tooth" deformation. Use digital calipers/profilometers for verification.
Root Cause Analysis
- Material flaws (42% of cases): Subsurface microcracks in over-tempered steel
- Misalignment: Concentrated 20°-45° abrasion patterns versus random spalling
New Sprockets Accelerating Chain Wear
New sprockets with hardness ≥5 HRC above chain links increase friction coefficients by 0.3–0.7. Replacing both components simultaneously reduces degradation by 68%.
Clicking vs. Grinding
| Sound Type | Frequency | Indicated Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Clicking | 2-5 kHz | Worn pin/bushing clearance >0.8mm |
| Grinding | <1.5 kHz | Metal-to-metal contact |
| Rhythmic grinding | 850 Hz | Sprocket misalignment (requires replacement within 80 hours) |
Lubrication Failure Correlation
The 2023 Komatsu Field Report found:
- Dry bushings increase impact forces by 240% at 5 mph
- Starved rollers produce 4-7 dB louder noise
- <250-hour regreasing intervals triple idler pitting risk
Preventive lubrication saves $17,300 vs. full undercarriage replacement. Spectral analysis detects failures 42 hours before visual confirmation.
Track Roller Wear Effects
Worn rollers (>8% diameter reduction) increase bushing stress by 300%. Measure quarterly to maintain even load distribution.
Idler Alignment Impact
3mm lateral misalignment per meter fractures sprocket tips within 200 hours. Verify alignment every 500 service hours with laser guides.
Fuel Consumption
+15% fuel use indicates chain inefficiency:
- Each 0.5mm bushing wear adds ~10 N·m drag torque
- Compare weekly telematics to manufacturer baselines
Hydraulic System Overload
Pressure spikes of 18-23% above optimal indicate:
- Misfitting chains forcing pumps to overwork
- Reservoir temperatures exceeding 200°F
Traction Loss Testing
Time 100-meter traversals at 75% throttle:
- 12%+ slower times indicate elongation
- Combine with DIN 22252-3 sprocket checks
OEM vs Aftermarket Parts
| Factor | OEM | Aftermarket |
|---|---|---|
| Unit cost | $480-$720 | $220-$380 |
| Downtime/failure | 2.1 hrs | 3.5 hrs |
| 12-month failure rate | 11% | 27% |
Aftermarket sprockets increase chain wear by 0.8 mm/month vs. OEM (CAT 320 excavator study).
Replacement Interval Optimization
- Overmaintenance (12% early replacements): +18% annual cost
- Delayed action (15% overdue): +22% repair costs from cascade failures
Predictive maintenance based on actual wear measurements reduces costs by 9% versus fixed schedules.
FAQ Section
What are the common signs of track chain wear?
The common signs include elongation exceeding operational limits, deterioration of link plates and bushings, and irregular tension loss patterns.
How can I measure the elongation of the track chain?
Elongation can be measured using calibrated tension gauges at three sections of the chain, comparing against operational thresholds based on machine weight class.
Why is it important to monitor sprocket tooth deformation?
Monitoring sprocket tooth deformation can prevent early "hook tooth" formation, reducing wear and mechanical failures in track systems.
How does lubrication failure affect track chain performance?
Lubrication failure can increase friction, leading to louder noise levels, and escalate wear and tear, ultimately resulting in costly repairs or replacements.
Table of Contents
- Elongation Measurement Thresholds
- Visual Inspection of Link Plates and Bushings
- Premature Track Tension Loss Patterns
- DIN 22252-3 Standard for Sprocket Profile Checks
- Root Cause Analysis
- New Sprockets Accelerating Chain Wear
- Clicking vs. Grinding
- Lubrication Failure Correlation
- Track Roller Wear Effects
- Idler Alignment Impact
- Fuel Consumption
- Hydraulic System Overload
- Traction Loss Testing
- OEM vs Aftermarket Parts
- Replacement Interval Optimization
- FAQ Section