Impact of Terrain on Excavators Undercarriage Wear
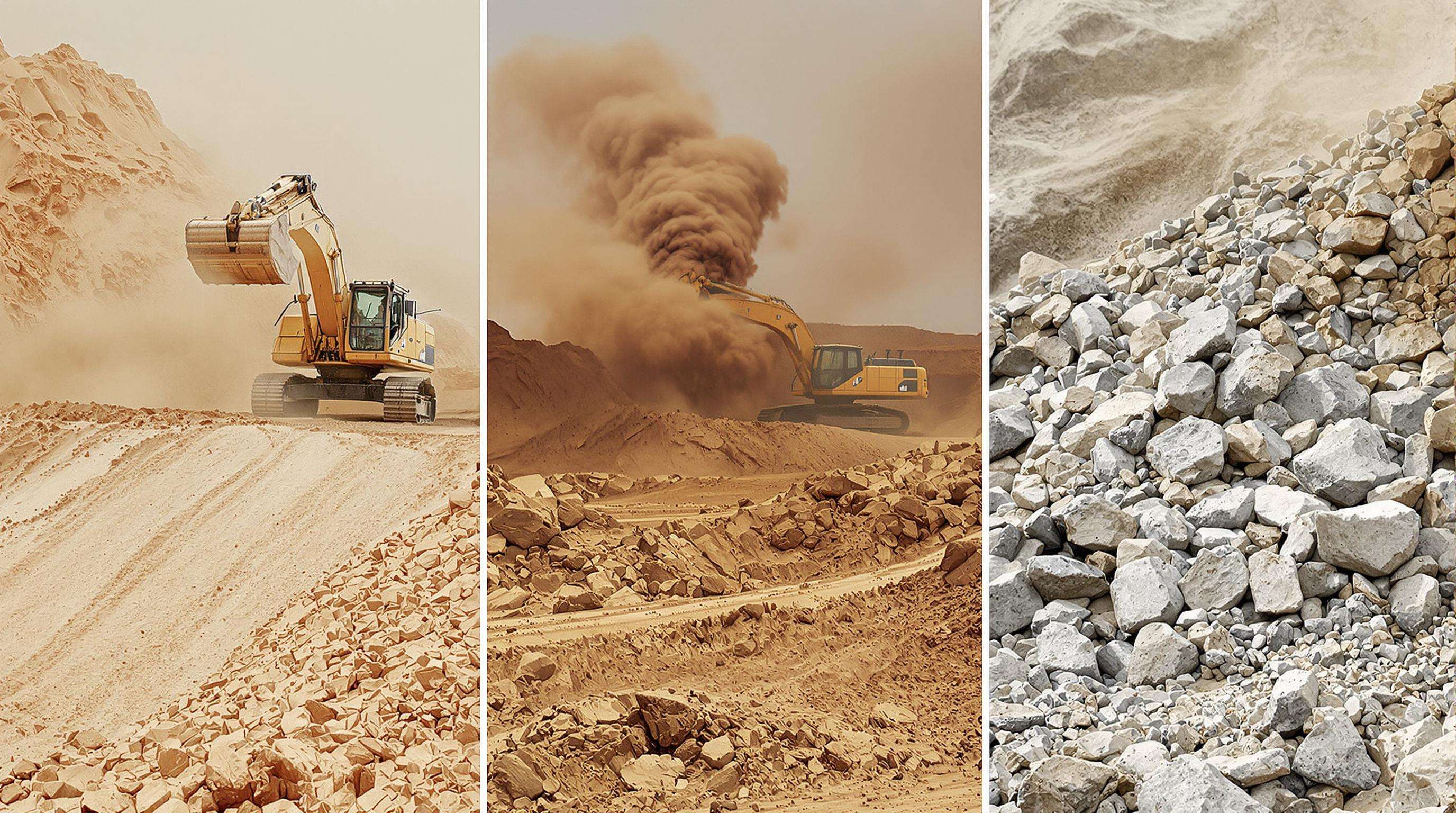

Abrasive Ground Conditions and Component Erosion
Aggressive terrains such as sandy deserts or construction sites with a high quartz content increase undercarriage wear by 18-34% over clay (NIST 2023). Dust abrades pin-and-bushing clearances in track chain joints and roller bearings for 0.5-1.2 mm every month. Track shoes wear down 40% faster in high silica environments, needing to be replaced every 1,200-1,500 hours instead of every 2,000 hours. Operators report annual premature wear costs of up to $12k/machine as a result of accelerated roller flange wear and idler wheel seizures.
Mud Contamination Accelerating Wear Patterns
Water saturated soil results to corrosive slurry that pass under-carriage seals combines mechanical with electrochemical attack. Mud increases the wear rate at pivot points by 3x due to its retention of sharp debris, with a 2022 study reporting that 83% of track link failures in swampy conditions was induced by mud displacement of lubrication. Swelling moisture induces galvanic corrosion (track chain connectors wear 30% more rapidly). Daily cleaning cuts roller bearing replacements by 60pct, as caked mud adds 18degC to running temperatures.
Rocky Surface Impact on Track Chain Longevity
Granite and basalt terrain exert 2,100-3,400 psi impact forces on track components, causing:
- Sprocket tooth deformation (0.3mm per 500 hours)
- Track link cracks from stress concentrations
- Roller shell ovalization, reducing load distribution efficiency
Machines in quarry applications demonstrate 22% shorter track chain lifespans than those in urban excavations. Operators mitigate damage by maintaining 25-30mm track shoe penetration depth, distributing forces across 43% more contact points.
Track Tension Dynamics in Undercarriage Degradation
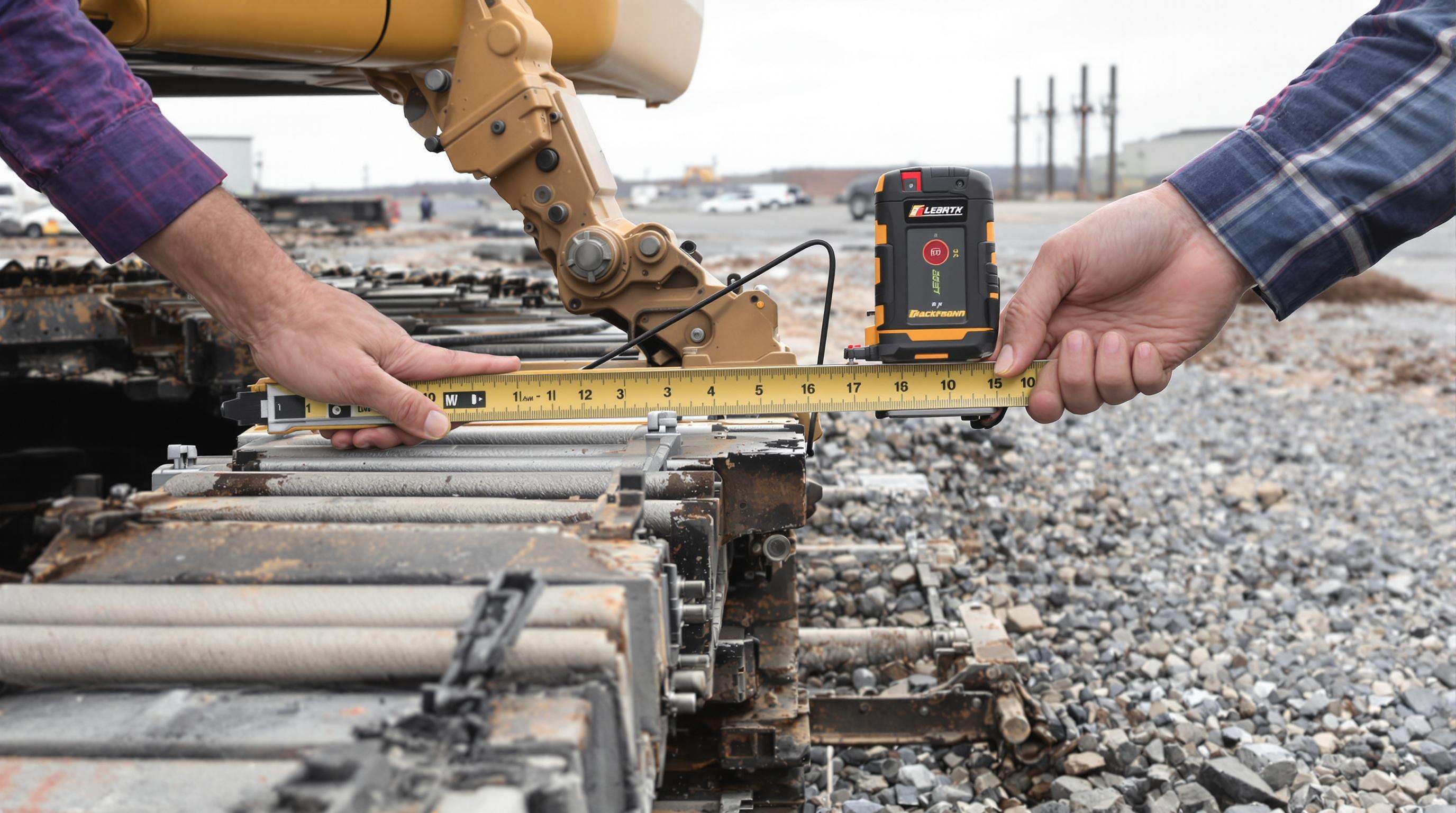

Optimal Tension Parameters for Different Terrains
Proper track tension varies by terrain:
- Loose sand/clay: 15-25 mm sag prevents soil compaction resistance
-
Compacted gravel: 5-10 mm sag minimizes chain oscillation
Manufacturers recommend: - Rubber tracks: 10-15% sag in soft terrain
- Steel tracks: 8-12 mm vertical deflection on rocky substrates
Daily temperature fluctuations can alter track length by 2-3%, requiring seasonal recalibration.
Consequences of Improper Track Sag Adjustment
Over-tightened tracks generate 18-22% higher roller loads (2023 excavator telemetry studies), accelerating bushing wear. Excessively loose tracks cause:
- Premature guide lug wear
- 30-40% faster idler wheel bearing failure
- Track derailment risks averaging $8,500 per incident (Equipment Maintenance Journal 2024)
Field-Proven Tension Calibration Techniques
Operators maintain precision tension using:
- Straightedge measurement: 1m bar with laser distance sensors (±0.5mm accuracy)
- Grease pressure monitoring: 150-180 psi during adjustments
- Dynamic testing: Verify OEM torque specs after 15-minute warmup
Bimonthly digital gauge checks reduce tension-related replacements by 60%.
Operator Practices Affecting Excavators Undercarriage Wear
Pivoting vs Straight-Line Movement Wear Comparison
Pivoting maneuvers accelerate wear 2.3X faster than straight-line operation (ICM 2023). Rotational forces grind chain links against sprockets, creating uneven contact in 250-400 hours. Straight-path travel extends component lifespan by 35%-41%. Reduce pivot wear by:
- Minimizing directional changes
- Maintaining <2 mph turning speeds
- Avoiding stationary "spot turns"
Load Management Strategies for Reduced Stress
Exceeding bucket capacity by 15% increases roller flange wear by 62% in clay soils (CEMA 2024). Effective techniques:
| Practice | Stress Reduction | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Partial bucket loading | 28% | $4,200 |
| Counterbalance usage | 19% | $2,800 |
| Slope-ascent reversing | 33% | $5,100 |
Engage auto-idle systems and verify loads via onboard telematics.
Preventive Maintenance Combatting Undercarriage Wear
Bi-Weekly Inspection Protocols
Measure track shoe thickness, bushing deformation, and roller flange wear. Early detection reduces replacements by 45% annually (Heavy Equipment Maintenance Audits 2024).
High-Pressure Cleaning Standards
3,000 PSI washes remove abrasive particles. Daily protocols extend track link life by 28%. Prioritize cleaning within 100 hours in saline environments.
Specialized Lubricants for Joint Protection
Lithium-complex greases resist water washout. Automated systems reduce pin/bushing wear by 63% versus manual applications.
Wear Measurement Tools
Digital calipers track sprocket tooth curvature. Replace components at 15% diameter loss or exposed core material.
Material Science in Undercarriage Wear Resistance
Hardfacing Technologies
Chromium carbide overlays reduce abrasive wear by 40-60% (Journal of Terramechanics 2023). Laser-clad hardfacing extends lifespans beyond 8,000 hours.
Sealed Lubrication vs Open Bushing Systems
Sealed systems reduce joint wear by 68% (Equipment Maintenance Quarterly 2022), maintaining viscosity for 350-500 hours versus 120 hours for open designs.
Economic Analysis of Undercarriage Wear Prevention
Cost Comparison: Maintenance vs Replacement
Preventative maintenance costs under 20% of operating budgets, while reactive repairs average $10,000 per incident. Proactive programs reduce lifetime costs by 30-45% and extend undercarriage lifespan by 40-60%.
FAQs
What factors contribute to excavator undercarriage wear?
Terrain, track tension, operator practices, and maintenance are key factors affecting wear.
How can track tension be optimized for different terrains?
Track tension varies; loose terrain needs more sag, while compact terrain requires less.
What maintenance practices help combat undercarriage wear?
Regular inspections, cleaning, specialized lubricants, and wear measurements are effective.
Table of Contents
- Impact of Terrain on Excavators Undercarriage Wear
- Track Tension Dynamics in Undercarriage Degradation
- Operator Practices Affecting Excavators Undercarriage Wear
- Preventive Maintenance Combatting Undercarriage Wear
- Material Science in Undercarriage Wear Resistance
- Economic Analysis of Undercarriage Wear Prevention
- FAQs