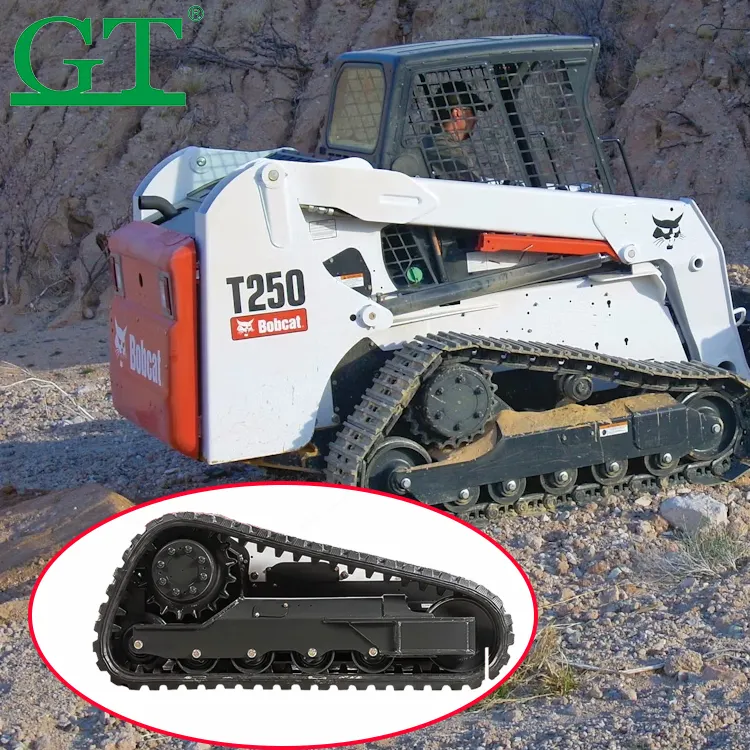
Defining OEM and Aftermarket Undercarriage Components
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Specifications
The OEM have strict engineering standards which are followed during the manufacturing of these undercarriage parts. Terms and conditions It determines metallurgical composition, dimensional tolerances (±0.05mm) as well as stressrelieving heat-treatment schedules for track chains, rollers and idlers. They are proprietary designs not available from engine manufacturers and have proven to be reliable after thorough testing. OEM requirements commonly require chrome-molybdenum alloy steel material with specified heat treatment hardening above 50 on the Rockwell C scale for wear critical parts.
Aftermarket Parts Manufacturing Processes
Aftermarket undercarriage parts are third-party manufactured replicas developed by reverse-engineered specifications. Companies that are worth their salt are using A572 steel or better and using the same forging and quenching procedures to OEM standards. Differences include wider tolerances (±0.2mm) for future compatibility across generations of equipment and faster production times focusing on volume efficiency. Serious manufacturers do perform strength and hardness testing, although the method used will differ according to what a machine shop can or cannot provide without having the OEM’s contracted validation information. Some manufacturers produce high-quality aftermarket replacements that are designed to prevent these failures in the first place.
Quality Comparison: OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Durability

Metallurgical Composition Standards Analysis
OEM undercarriage parts use a steel alloy selected for high-impact loading and stress while meeting stringent equipment specifications such as ASTM A572 Grade 50. Independent Third-Party inspection knuckle load tests show aftermarket options typically use off the shelf grades such as A36 steel – with 12-18% lower yield strength. This discrepancy has a direct effect on resistance to plastic deformation under high stress conditions like rock cutting.
Stress Testing Protocols for Track Chains
Manufacturers subject OEM track chains to multi-stage validation cycles, including accelerated wear simulations replicating 10,000-hour operational loads. Independent studies show aftermarket components frequently bypass critical fatigue testing phases, with 34% of sampled parts failing ASME B30.26 endurance benchmarks within 6,000 hours. OEM designs demonstrate 40% greater crack propagation resistance under cyclical loading.
Field Performance in Mining Operations
Mining environments subject material to shockingly extreme conditions in which it’s impossible to ignore quality differences. Based on data from 78 surface mines, aftermarket track shoes must be replaced 15%-30% more often than OEM track shoes when moving 18-24t/h loads of crushed ore. Shovel belt case study - spalled bushings and premature pin failures 62% of afterhours downtime with a successful development of an automated tooling system.
Lifespan Metrics Across Operating Conditions
Compares 10,000 hour mixed terrain life of OEM and aftermarket undercarriage systems: OEM undercarriage systems retain 80% structural integrity, aftermarket alternatives retain 50-70% structural integrity. In severe abrasion (i.e. oil sands) the variance further increases - OEM parts provide 3,200 more operating hours before mandatory replacement. Although the aftermarket components exhibit high performance coincidence stagnates in mild conditions (≤150 kN/m² ground pressure) since their efficiency and convergence performance decrease exponentially in impact loading conditions.
Cost Analysis of OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Solutions
Upfront Purchase Price Breakdown
As an essential aspect of spare and replacement parts and accessories for at least two reasons, the OEM undercarriage components are often premium priced because of the brand of the manufacturer, and because of the specialized tools and certifications involved in their manufacture. On the other hand, the costs for aftermarket are much cheaper, 20-50% less than the initial cost due to not having to pay the licensing fees, using mass volume manufacturing, etc. This price gap is particularly important in case of track chains and rollers used in mining, where massive replacements are involved.
Long-Term Maintenance Cost Projections
While OEM-style parts offer engineered longevity, A quality aftermarket alternative is made from modern metallurgy. Industry data shows aftermarket track chain alternatives can lower the annual cost of maintenance on track type machines by 15-30%, when it is sized correctly for the working environment. But off-brand quality may raise long-term costs - 22% of equipment users do cite greater failure rates in tough, high-impact conditions. Suppliers still must be properly vetted to ensure reliable cost.
Resale Value Impact on Heavy Equipment
Equipment with OEM undercarriages also has 8-12% higher resale value based on auction analytics. This premium results from buyers’ faith in factory tolerances and recorded maintenance. This is particularly true for dozers in overburden removal applications; where the condition of undercarriage plays a pivotal role in valuation assessments and thus the degree of asset depreciation.
| Cost Factor | OEM Advantage | Aftermarket Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower (for quality assurance) | Higher savings |
| Lifetime Maintenance | Predictable servicing | Potential for optimized TCO |
| Residual Value Retention | Significant premium | Requires documentation proof |
Warranty Considerations for Undercarriage Replacements
OEM Factory Coverage Limitations
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) warranties will generally cover defects in materials or quality but are very restrictive. Most commonly, coverages range from 1-2 years or 2000-3000 machine hours, less wear-related failures - the leading problem contributing to undercarriage wear. There are strict requirements — the base systems must be installed by factory-certified technicians and come with logs detailing maintenance. Failure to do so will cancel the warranty and all costs for early replacement will be at the operator's expense.
Aftermarket Parts Guarantee Structures
After market vendors offer more flexible warranties, and high quality providers will meet or exceed OEM periods, up to 3 years or 4000 run hours. Most policies also cover manufacturing defects, as well as normal wear and tear. Contrary to OEM restrictions, claims procedures allow for third-party installations IF they are installed by certified technicians. But warranty coverage also varies significantly; operators should confirm what is not covered, such as harsh, abrasive ground or attachments.
Availability Challenges: OEM vs Aftermarket Lead Times

Securing undercarriage components promptly presents distinct challenges between OEM and aftermarket channels. Lead time discrepancies often force fleet decisions balancing downtime costs against replacement quality.
Global Supply Chain Complexities
OEM parts face multi-layered logistics hurdles—centralized manufacturing, single-source dependencies, and cross-continental shipping routes. Production bottlenecks compound delays when manufacturers prioritize new equipment over replacement components. Older excavator models risk obsolescence with discontinued parts, creating 6-12 week gaps that stall mining operations.
Localized Aftermarket Production Advantages
Local aftermarket manufacturers speed availability through local manufacturing hubs, which usually result in parts in 1-3 weeks. Modular manufacturing processes respond to demand variation and work in conjunction with standard operations to ensure quality at 80% of typical undercarriage responses. Being close to the mines lowers shipping costs on average by 18%, and the majority of distributors carry in-stock ready to ship supplies of critical items such as link assemblies, and rollers.
Compatibility Factors for Excavator and Dozer Undercarriages
Precision Fitment in OEM Components
Original equipment manufacturer undercarriage parts undergo rigorous dimensional validation for specific equipment models. This precision ensures critical components like track links and rollers maintain exact factory tolerances down to ±0.2mm measurement accuracy. Such micrometric control prevents abnormal friction points during operation while preserving hydraulic alignment integrity.
Aftermarket Tolerance Range Solutions
Aftermarket manufacturers offset compatibility challenges through strategic tolerance allowances. Engineered dimensional variances of ±1.5mm enable single replacement parts to function across multiple machine generations through modular shim adaptation systems. Third-party producers implement ISO-certified interchangeability testing protocols that validate safety margins under maximum load conditions.
Retrofitting Challenges in Mixed Systems
Mixing OEM and aftermarket parts results in intricate geometric interferences in track chain assemblies. Mixed undercarriage types show a 23% higher speed on wear development according to earth moving equipment maintenance reports. The main issue is that there are mismatched hardness between the original and after market parts — mainly in the area of the bushings and sprocket teeth. For mitigation, the point scientist works together with the instrument scientist during assembly studying pressure distribution using dedicated laser alignment tools.
Strategic Selection Criteria for Fleet Managers
Cost-Benefit Analysis Frameworks
Fleet managers need objective ways to evaluate OEM vs. aftermarket undercarriage choices. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) models deliver detailed financial analysis by analyzing upfront costs versus life and operating costs. The data is clear: OEM parts tend to have initial cost deltas of between 20-35% but better long-term economics for high-utilization fleets. The application of weighted multi-criteria decision analysis methods allows for a consistent assessment considering operational needs such as safety margins and downtime risks.
Equipment Utilization Rate Considerations
The optimal undercarriage configuration is exclusively dictated by the hourly operational intensity. For more than 3,000 annual operating hours, the mine operation study found premium OEM parts offer the best value for money despite their higher purchase price. On the other hand, low-utilization products (less than 1,500 hours/year) take advantage of aftermarket options (with 15-30% cost savings). Telematics data can also allow fleet managers to compare duty-cycle ratings published by a manufacturer with actual usage, ensuring that specifications are based on the true loading pattern and so either over-engineering or early wear can be avoided.
FAQ
What are the main differences between OEM and aftermarket undercarriage components?
OEM components are manufactured according to strict proprietary specifications and often have higher durability and reliability standards. Aftermarket parts are replicas produced with broader tolerances for compatibility with multiple equipment generations.
Are aftermarket undercarriage parts cheaper than OEM parts?
Yes, aftermarket parts are generally 20-50% less expensive upfront due to volume manufacturing and the absence of licensing fees.
How do OEM and aftermarket warranties differ for undercarriage components?
OEM warranties typically cover 1-2 years or 2000-3000 machine hours and require certified installation. Aftermarket warranties are usually more flexible, covering up to 3 years or 4000 hours, and allow for third-party installations as long as they're done by certified technicians.
What are the lead times for OEM vs aftermarket undercarriage parts?
OEM parts often face longer lead times due to centralized manufacturing and potential logistics hurdles, taking 6-12 weeks. Aftermarket parts are more readily available, often within 1-3 weeks, thanks to localized production.
Table of Contents
- Defining OEM and Aftermarket Undercarriage Components
- Quality Comparison: OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Durability
- Cost Analysis of OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Solutions
- Warranty Considerations for Undercarriage Replacements
- Availability Challenges: OEM vs Aftermarket Lead Times
- Compatibility Factors for Excavator and Dozer Undercarriages
- Strategic Selection Criteria for Fleet Managers
- FAQ