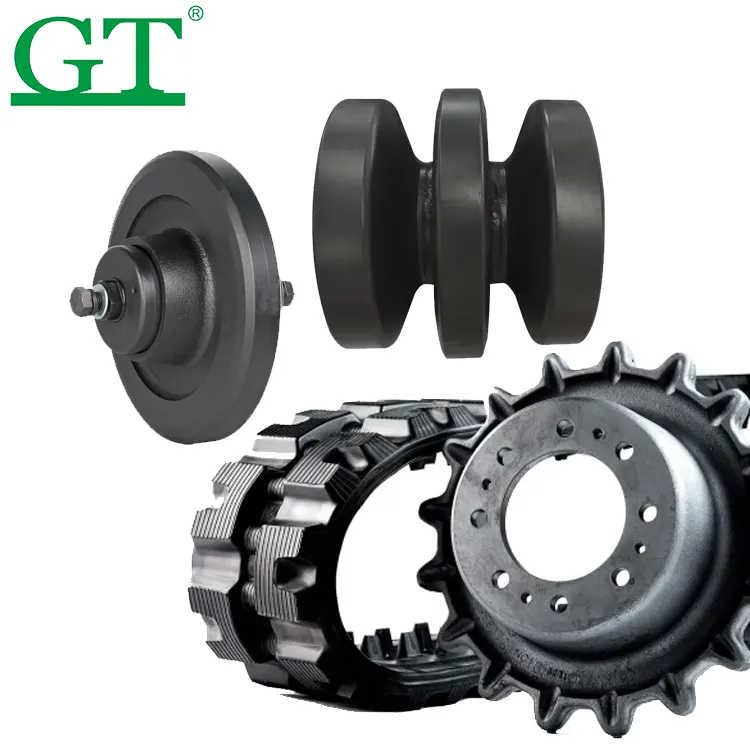
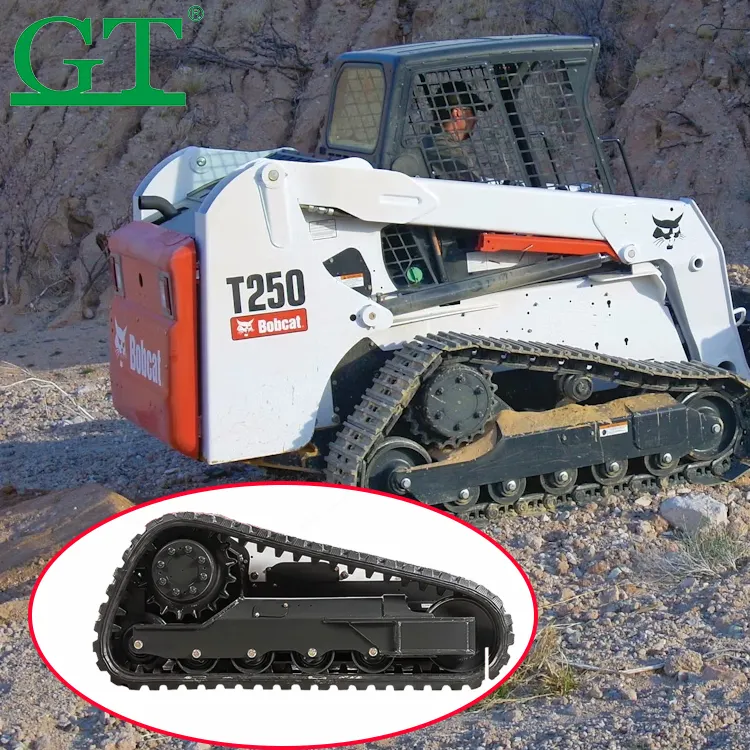
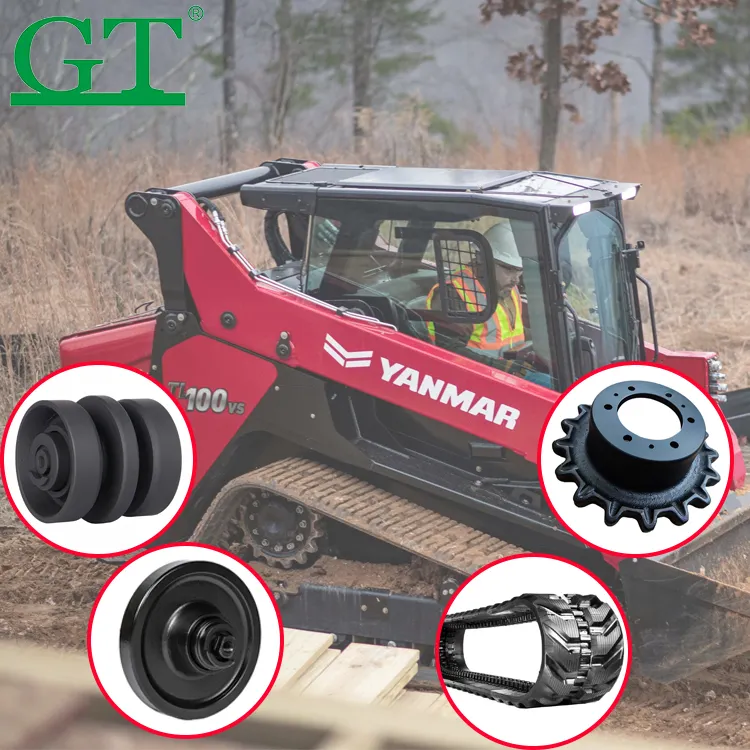
Understanding Excavator Undercarriage Parts and Their Functions
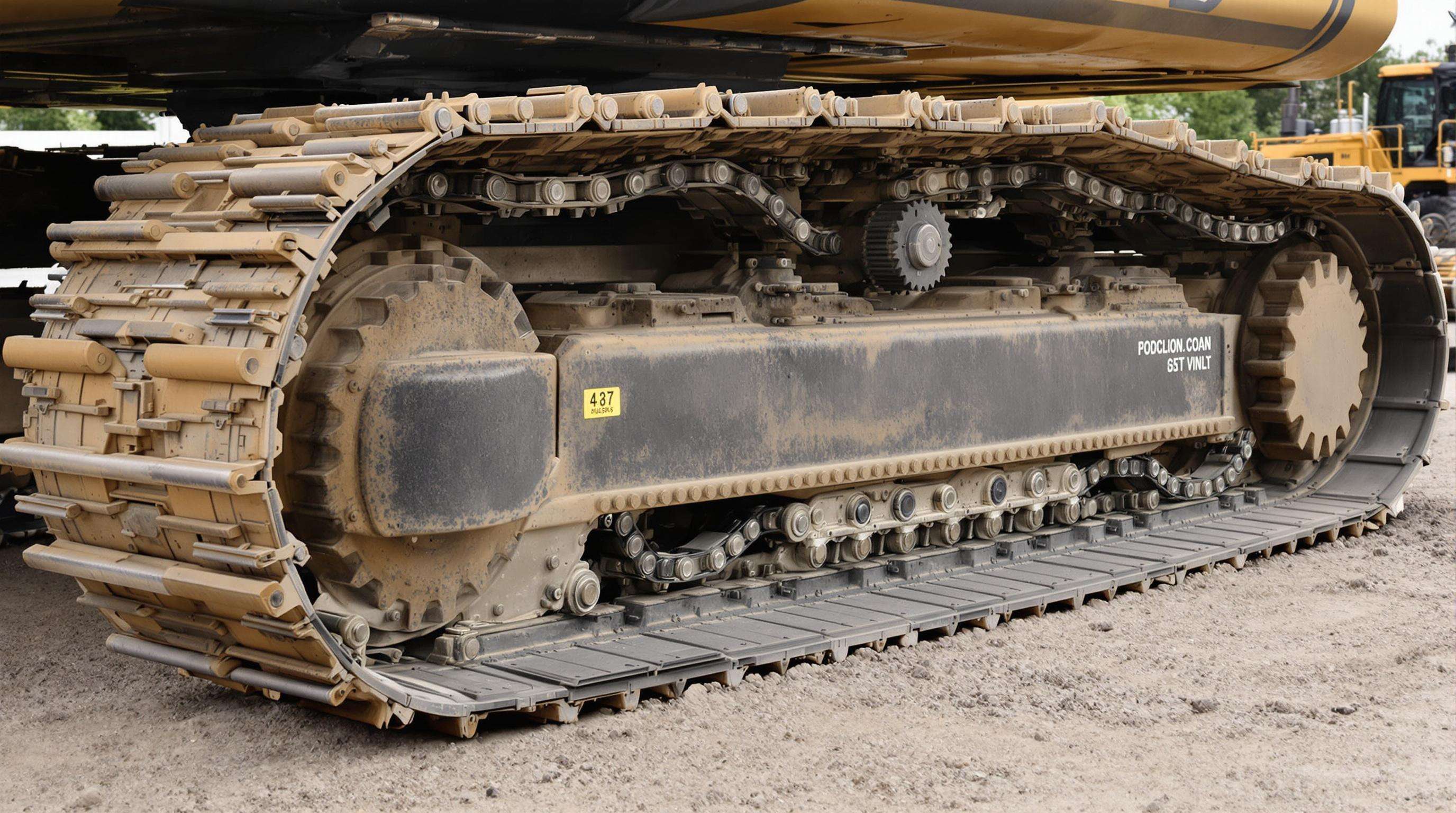

Core Components: Track Chains, Rollers, and Sprockets Explained
The excavator undercarriage forms the mobility foundation, with track chains linking plates into continuous loops. Rollers distribute weight evenly while guiding movement, and sprockets engage chain links to transfer power from the final drive. Proper alignment prevents premature wear during digging cycles.
Material Hardness Requirements for Dozers Undercarriage Parts
Abrasive terrains demand high hardness (350–450 HB) in rollers and links to resist pitting and deformation. Case-hardened steel alloys balance toughness with wear resistance—essential for rocky or demolition-heavy sites.
Load Capacity Considerations in Track Pad Selection
Proper pad selection ensures optimal ground pressure distribution. Engineers match pad size to machine weight—larger pads reduce ground pressure by up to 24% on soft soils. Load ratings should exceed excavator weight plus bucket payload to avoid stress fractures.
Key Performance Indicators for Track Pads
| Metric | Soft Soil | Rocky Terrain |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal Width | 24–32 inches | 18–22 inches |
| Ground Pressure | ≈8 PSI | ≈12 PSI |
| Carbon Steel Thickness | ≥0.8 inches | ≥1.2 inches |
Heat-treated manganese steel pads extend lifespan by 30% compared to standard options by maintaining shape under cyclical loads.
Matching Undercarriage Parts to Machine Type and Application
General-Duty vs Heavy-Duty Undercarriage Systems Compared
General-duty systems (350–400 HB) suit light applications like grading, while heavy-duty systems (450–500 BHN) handle mining with 30–50% higher impact resistance. Forging enhances durability, increasing lifespan by 15–20% over cast parts in high-stress conditions.
Optimizing Track Shoe Selection for Construction Environments
Wide track shoes (18–24 inches) reduce sinkage in mud by 40%. For rocky terrain, triple-bar steel shoes minimize rock penetration while maintaining traction. Modern sealed pivot joints reduce abrasive ingress by 70%, extending service intervals to 2,500–3,000 hours.
Case Study: Mining vs Urban Excavation Configurations
| Parameter | Mining Configuration | Urban Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Track Width | 32" (813 mm) | 24" (610 mm) |
| Ground Pressure | 12 psi | 6 psi |
| Component Sealing | Quad-lip labyrinth seals | Double-sealed waterproofing |
| Maintenance Cycle | 500-hour inspections | 250-hour inspections |
Mining setups prioritize load dispersion, while urban designs focus on maneuverability and vibration control. Mismatched configurations increase repair costs by 22%.
Undercarriage Parts Types: Extended-Life vs Standard Components
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Heavy-Duty Extended-Life Systems
Extended-life systems last 20–40% longer, reducing downtime by 30%. Though initial costs are 15–25% higher, high-intensity applications like mining benefit from lower long-term operational expenses.
Precision Manufacturing Differences in OEM Components
OEM forgings achieve 12% greater material density than standard castings, enhancing durability. Tolerances of 0.01–0.05mm ensure 15–18% greater hardness, critical for abrasive terrains.
OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Parts Selection Strategy
Durability Comparison: Manufacturer Specifications vs Third-Party
OEM track chains average 6,200 operational hours versus 4,300 for aftermarket alternatives, with boron steel inserts extending lifespan in mining by 42%.
Warranty Implications for Excavators Undercarriage Replacements
OEM warranties cover 3–5 years, while aftermarket options average 12–18 months. Non-OEM parts void manufacturer warranties in 83% of cases, potentially costing $18k+ per incident.
Industry Paradox: When Cheaper Parts Increase Long-Term Costs
Aftermarket sprockets require replacement every 14 months versus OEM's 26 months, leading to 18% higher lifetime expenses in mixed-terrain operations.
Terrain-Specific Selection of Dozers Undercarriage Components
Muddy vs Rocky Surfaces: Track Width Adaptation Guide
For mud, 36-inch tracks reduce ground pressure to 4.5 psi, while 20-inch hardened steel tracks improve grip on rocks, decreasing penetration by 28%. Research shows wider track shoes reduce slippage by 41% in swamps.
Preventing Premature Wear Through Environmental Compatibility
| Factor | Muddy Terrain | Rocky Terrain |
|---|---|---|
| Track Material | Sealed polyurethane chains | Case-hardened alloy steel |
| Lubrication System | Pressurized grease injection | Dry pin bushings |
| Ground Clearance | 18–22 inches | 14–16 inches |
Coastal environments require zinc-nickel-coated rollers to combat 53% faster corrosion rates. For quarries, forged links last 72% longer with 55 HRC hardness.
Evaluating Undercarriage Parts Suppliers: Quality Benchmarks
Certification Requirements for Replacement Track Assemblies
Prioritize ISO 9001 and 14001-certified suppliers. CE-marked parts meet EU safety standards, reducing premature wear risks by 32%. Verify batch testing documentation before purchase.
Supplier Reputation Analysis in Heavy Machinery Sector
Choose suppliers with <0.5% defect rates and proven mining or infrastructure experience. Reliable manufacturers provide material reports and partner with major operators.
Warranty Duration as Indicator of Component Durability
Quality sprockets and rollers typically carry 3–5 year warranties, versus 1–2 years for economy parts. Ensure warranty terms clearly define coverage limits.
FAQ: Excavator Undercarriage Parts
What are the main components of an excavator undercarriage?
The main components are track chains, rollers, and sprockets, which work together to provide mobility and power transmission for the excavator.
How do material hardness requirements affect undercarriage parts?
Material hardness is crucial in resisting wear and deformation, especially in abrasive terrains, ensuring the longevity of components like rollers and links.
Why is it important to match undercarriage parts to the machine type and application?
Matching ensures optimal performance, reduces wear, and prevents costly repairs by ensuring parts are suited to specific tasks and environments.
What are the advantages of using extended-life undercarriage systems?
Extended-life systems last longer and reduce downtime, which can offset higher initial costs in high-intensity operations like mining.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Excavator Undercarriage Parts and Their Functions
- Matching Undercarriage Parts to Machine Type and Application
- Undercarriage Parts Types: Extended-Life vs Standard Components
- OEM vs Aftermarket Undercarriage Parts Selection Strategy
- Terrain-Specific Selection of Dozers Undercarriage Components
- Evaluating Undercarriage Parts Suppliers: Quality Benchmarks
- FAQ: Excavator Undercarriage Parts