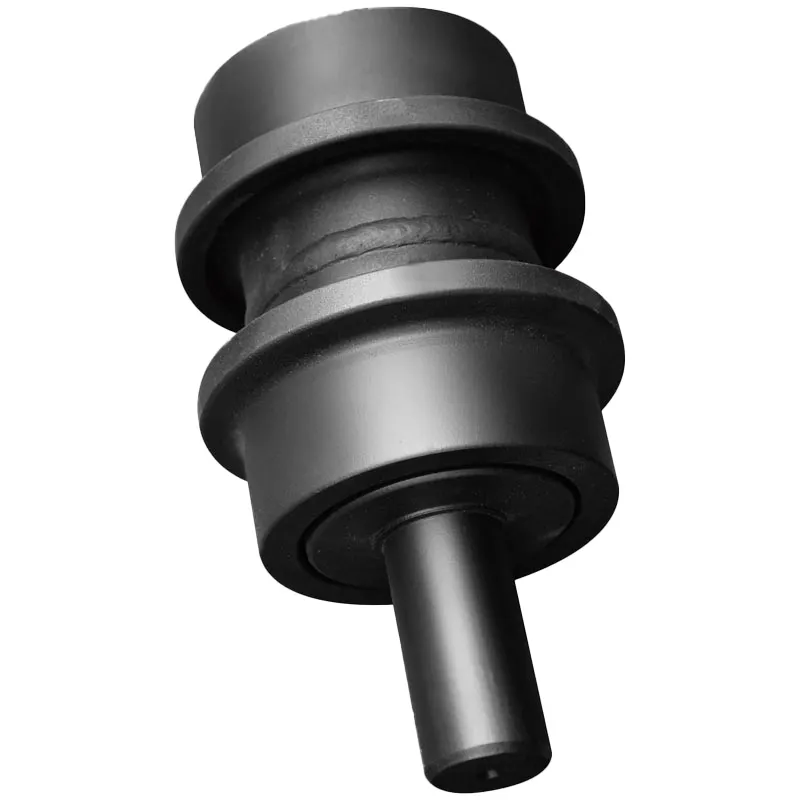
Understanding the Carrier Roller and Its Function in Undercarriage Systems
The Function and Importance of Carrier Rollers in an Excavator Undercarriage
Carrier rollers sit on the upper part of track frames in heavy equipment. These parts basically hold up the top section of the track chain as it moves between the sprocket and idler point. They keep everything lined up properly and stop too much slack from forming. If carrier rollers weren't there, tracks tend to droop down which causes more vibration throughout the machine, wears things out faster, and increases chances of the track coming off completely. The importance really stands out in machines with extended track frames or when working with heavy weights. Misalignment issues in these situations can seriously cut down how well the machine handles rough ground conditions. Some studies suggest maneuverability drops around 20 percent when alignment problems occur, though actual field experience often shows similar results without needing exact measurements.
How the Role of Carrier Rollers Supports Overall Machine Performance
Carrier rollers help keep track tension steady which makes machines run better and saves energy overall. These components cut down on friction where the track meets the undercarriage frame, so equipment moves more smoothly when doing tasks like grading or turning on site. When kept in good condition, rollers actually cut track wear down somewhere around 30 to 40 percent. That means sprockets and idlers last longer too. The way these rollers manage both direction control and weight distribution helps power get transferred efficiently to the ground surface, no matter what kind of terrain or workload changes happen during operation.
Location of Carrier Rollers in Tracked Machinery and Their Structural Integration
Carrier rollers sit on top part of the undercarriage area right between the sprocket and front idler. These components direct where the track chain goes back after it passes through, making sure it doesn't rub against the main frame of the machine. Today's roller designs incorporate hardened steel pins and stronger flange parts that stand up better against wear from dirt and rocks. Some newer machines even come with removable housing units so maintenance crews can get inside without tearing everything apart. When combined with those lower track rollers, carrier rollers share the weight distribution across all sections of the undercarriage, which helps prolong equipment life and keeps things running smoothly during operation.
Maintaining Track Tension and Alignment with Carrier Rollers
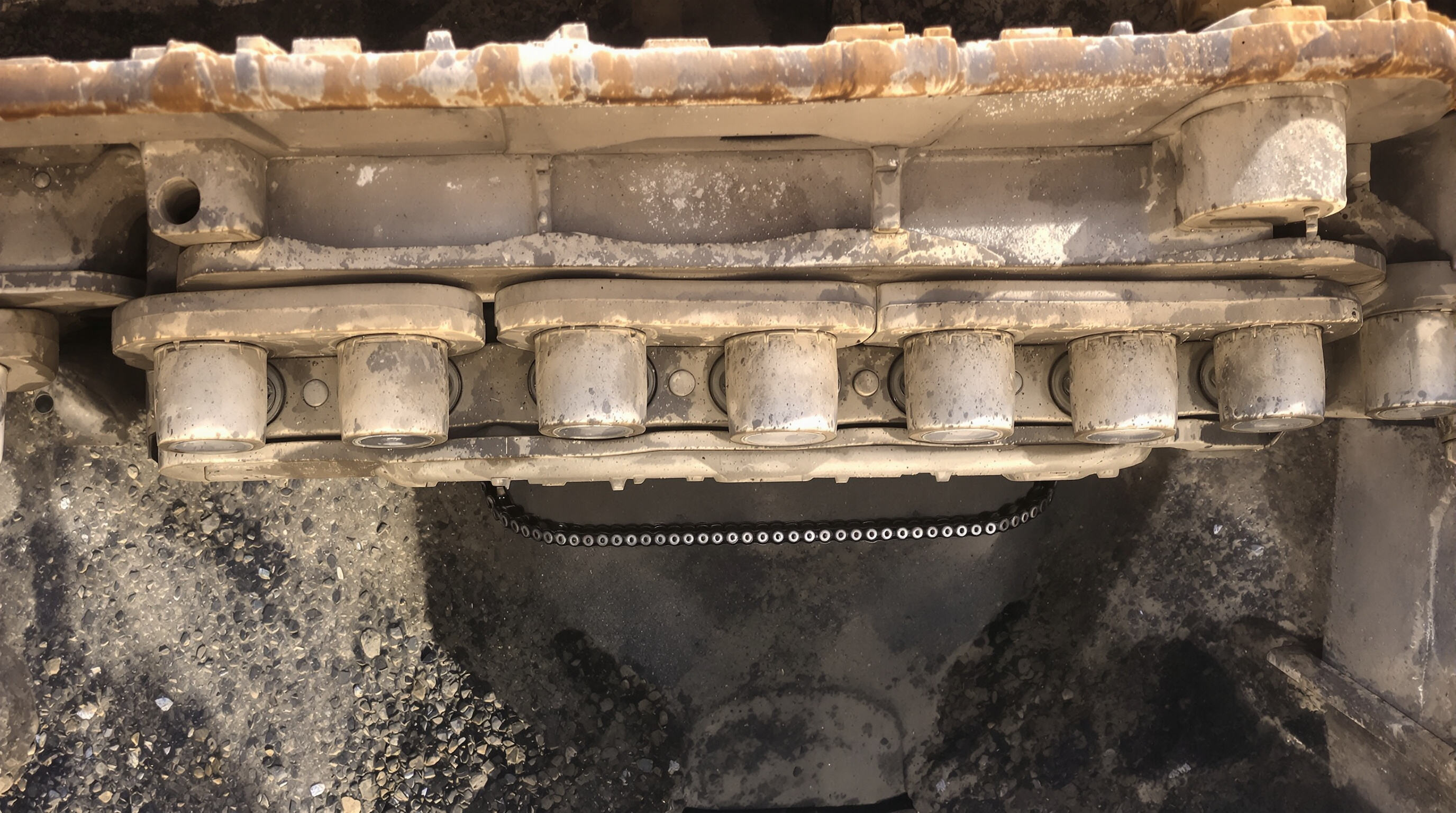

Role of Carrier Rollers in Track Tension and Alignment: Ensuring Smooth Track Travel
The carrier rollers play a key role in keeping the track chain stable. They maintain the right amount of tension and alignment while spreading out the weight across the upper frame so it doesn't sag down. When everything stays tight enough, the chain engages better with those sprockets and idler wheels, which means less slippage happening during operation and not as much wasted energy either. According to research published last year in the Heavy Machinery Journal, equipment with well maintained carrier roller tension showed around 18 percent less wear on the track chains than machines where maintenance was overlooked completely. That kind of difference adds up over time for operators looking to extend their machinery lifespan.
Interaction Between Carrier Rollers and Track Chains Under Dynamic Loads
When machines are under load, carrier rollers take the vertical force and let there be some side-to-side movement as equipment turns or moves over rough spots. This helps avoid those nasty stress points that break things. But here's the problem many operators face: constant bumps from rocky ground really takes a toll on the bearings over time. The flexibility starts to fade. Most people don't even realize their bearings are worn until they notice strange vibrations or hear odd noises coming from the tracks. And once that happens, components start failing way earlier than expected, which nobody wants when trying to keep operations running smoothly day after day.
Impact of Misaligned Carrier Rollers on Track Wear and Machine Efficiency
Misalignment causes uneven pressure across track links, accelerating wear on pins, bushings, and flanges. This increases friction and can raise fuel consumption by up to 9% (Construction Equipment Insights, 2023). If uncorrected, misalignment may lead to track derailments, which account for 23% of unplanned undercarriage-related downtime in tracked construction equipment.
Case Study: Reduced Downtime Through Optimized Carrier Roller Alignment
At a quarry somewhere in the northern US, they started checking carrier roller alignments every other week on all their 22 ton excavators back in late 2022. After running with this routine for about a year, the results were pretty impressive. Track problems causing equipment downtime dropped nearly half, around 41%, while those expensive track chains lasted almost 30% longer than before. The team used fancy laser tools and heat sensors to spot issues with bearings long before they became real problems. What this shows is that spending time on regular maintenance actually pays off big time when machines are working nonstop day after day.
Carrier Roller vs. Track Rollers: Key Differences in Function and Load Distribution
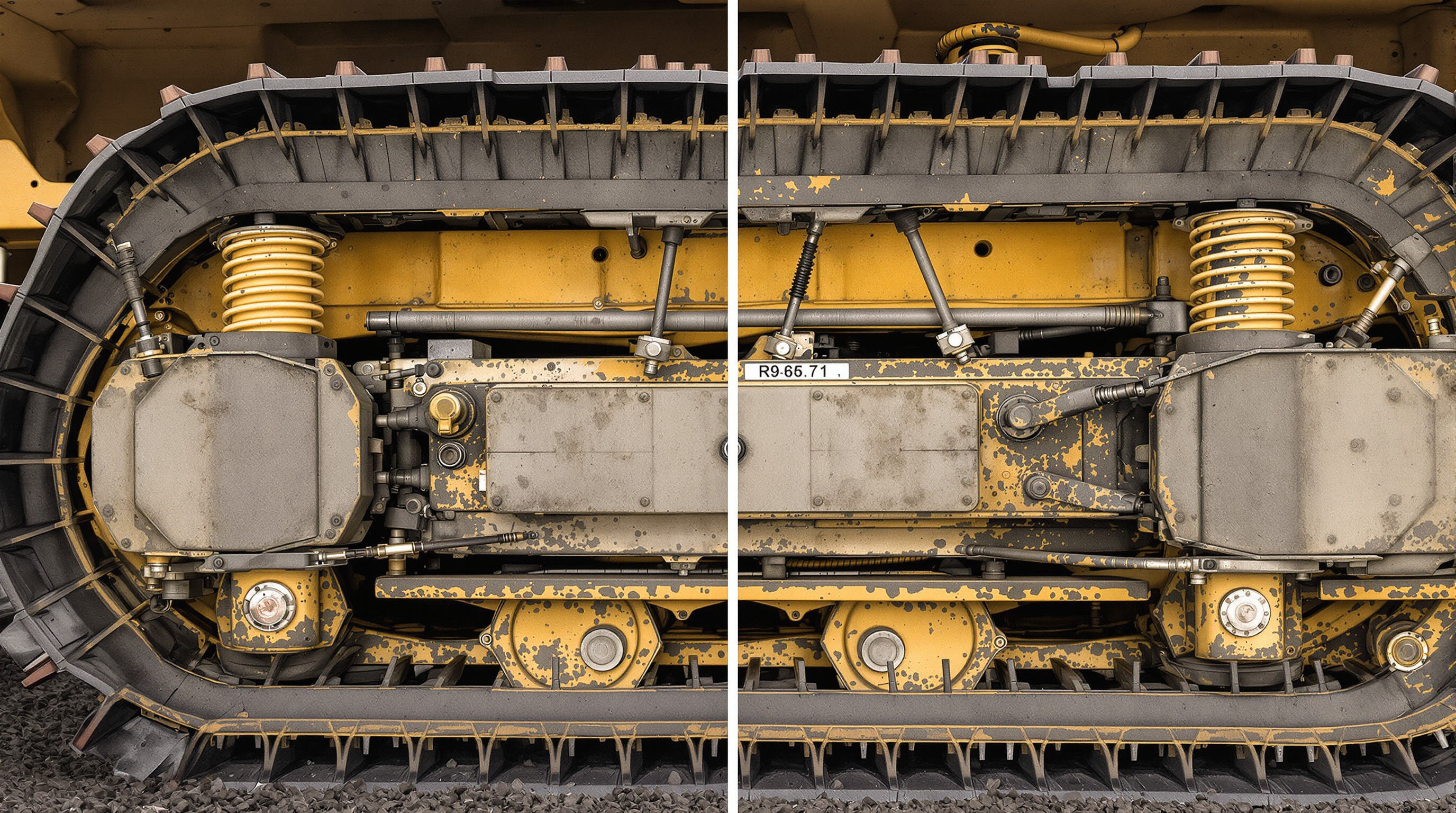

Difference Between Track Rollers and Carrier Rollers: Function and Placement
The difference between track rollers and carrier rollers matters quite a bit when it comes to heavy machinery operation. Track rollers sit right underneath the undercarriage structure and take on all the weight of the machine itself. This allows equipment to move smoothly even across rocky or uneven ground surfaces. Meanwhile, carrier rollers are positioned higher up on the main frame structure. Their job is to keep the track chain moving properly along its return path, which helps avoid excessive sagging and minimizes annoying vibrations during operation. Getting these mixed up when doing maintenance work often results in improper fixes that actually speed up wear and tear on the entire undercarriage system over time.
Types of Rollers in the Undercarriage System
The undercarriage relies on two key roller types:
- Track rollers (bottom rollers): Built to handle compressive loads from the machine’s weight.
- Carrier rollers (top rollers): Designed to manage track chain tension and maintain alignment.
Though they work together, their structural designs differ to meet unique operational demands.
Load Distribution Comparison: Carrier Roller vs. Track Roller Responsibilities
These components have complementary yet opposing load roles:
| Component | Primary Load Responsibility | Secondary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Track Roller | Supports 90–100% of machine weight | Reduces ground pressure |
| Carrier Roller | Manages track chain tension | Prevents track-to-frame contact |
While track rollers absorb terrain shocks, carrier rollers minimize track oscillation. This division enhances undercarriage durability and overall efficiency.
Wear Patterns and Proactive Maintenance for Carrier Roller Longevity
Wear and Maintenance of Carrier Rollers: Identifying Early Signs of Failure
Carrier rollers display specific wear indicators before failure. Watch for uneven tread wear, grinding noises, flange cracking, lateral play over 3mm, groove deformation, and corrosion pitting—especially in corrosive environments. Detecting these issues through biweekly inspections can cut replacement costs by up to 60% compared to reactive repairs.
Common Causes of Premature Carrier Roller Wear in Harsh Operating Conditions
Three main factors drive early wear:
- Abrasive contamination — Fine particles bypassing seals cause 78% of premature failures (Machinery Wear Analysis 2024)
- Improper track tension — Over-tightening increases roller side load by 40%
- Thermal stress — Repeated temperature changes degrade polymer seals
Mining operations experience wear rates three times higher than agricultural applications, underscoring the need for environment-specific maintenance.
Best Practices for Lubrication, Inspection, and Replacement Intervals
Follow this maintenance schedule to extend carrier roller life:
| Task | Frequency | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Grease replenishment | Every 50 operating hours | NLGI #2 lithium-complex grease |
| Seal inspection | Weekly | No visible cracks or hardening |
| Radial clearance check | Monthly | ±1.5mm tolerance |
Operators adhering to this protocol report 35% longer service intervals while meeting OEM performance standards.
Controversy Analysis: Scheduled Replacement vs. Condition-Based Maintenance
The industry debates optimal replacement strategies:
Scheduled replacement advocates emphasize predictable budgets and reduced risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Condition-based proponents highlight 28% cost savings through extended component life (Equipment Lifecycle Study 2023) and improved accuracy using real-time data from IoT-enabled rollers.
Leading manufacturers now offer hybrid programs combining scheduled inspections with sensor-driven alerts, resolving 63% of historical concerns in field trials.
Innovations in Carrier Roller Design: Sealing, Materials, and Smart Monitoring
Trend toward enhanced sealing and corrosion-resistant materials
Today's carrier rollers come equipped with sealing systems that really stand up against dirt and moisture ingress. Research published last year indicated that when engineers use these complex simulation tools for seal design, they actually get around a 40% boost in how long seals last in harsh conditions. Many manufacturers now pair dual-lip seals with special chromium molybdenum steel mixtures. This combination cuts down on corrosion problems significantly compared to older designs, giving equipment roughly two thousand extra operating hours before needing replacement parts.
Xiamen Globe Machine Coltd and advancements in sealed carrier roller technology
Manufacturers like Xiamen Globe Machine Coltd have developed sealed roller systems with triple-stage architectures, integrating nitrile rubber buffers and labyrinth-style grease chambers. Field tests show these designs reduce lubrication-related failures by 55% in mining applications, while self-cleaning flange configurations prevent mud buildup between rollers and track chains.
Integration of smart sensors for real-time carrier roller monitoring
IoT-enabled carrier rollers with embedded temperature and vibration sensors are transforming maintenance. Centralized dashboards deliver real-time bearing health data, allowing operators to schedule replacements before failure. Early adopters report 35% fewer unplanned downtime events, with predictive algorithms analyzing load patterns to optimize performance under variable operating stresses.
FAQ Section
Q1: What role do carrier rollers play in heavy machinery?
A1: Carrier rollers help maintain track tension and alignment, reducing vibration and wear in heavy machinery, and improving maneuverability and overall machine efficiency.
Q2: How do carrier rollers differ from track rollers in the undercarriage system?
A2: Carrier rollers manage track chain tension and alignment, located above the undercarriage, while track rollers support the machine's weight from below and reduce ground pressure.
Q3: What causes premature carrier roller wear?
A3: Premature wear can be caused by abrasive contamination, improper track tension, and thermal stress. Regular maintenance and appropriate environmental adaptations can mitigate these factors.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Carrier Roller and Its Function in Undercarriage Systems
-
Maintaining Track Tension and Alignment with Carrier Rollers
- Role of Carrier Rollers in Track Tension and Alignment: Ensuring Smooth Track Travel
- Interaction Between Carrier Rollers and Track Chains Under Dynamic Loads
- Impact of Misaligned Carrier Rollers on Track Wear and Machine Efficiency
- Case Study: Reduced Downtime Through Optimized Carrier Roller Alignment
- Carrier Roller vs. Track Rollers: Key Differences in Function and Load Distribution
- Wear Patterns and Proactive Maintenance for Carrier Roller Longevity
- Innovations in Carrier Roller Design: Sealing, Materials, and Smart Monitoring
- FAQ Section